Surgical Solutions for Lymphedema Treatment
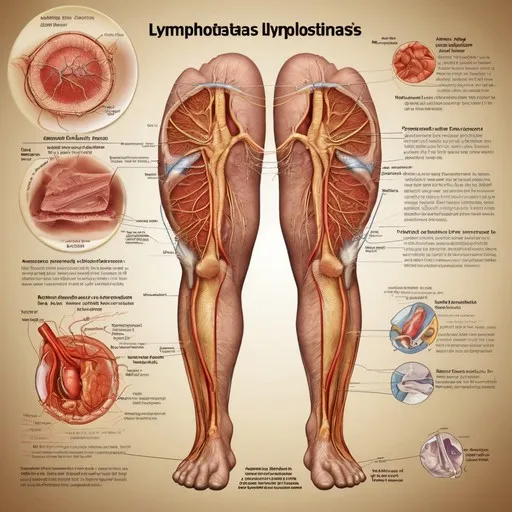
Lymphedema, often caused by cancer treatments like lymph node removal or radiation therapy, can be effectively managed with surgical interventions. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for the best outcomes.
Early-Stage Lymphedema: Importance of Prompt Action
At the earliest stages, lymphedema might not show visible swelling. Advanced diagnostic methods, such as fluorescent lymphography, can identify issues before they worsen. Surgical intervention at this stage can prevent irreversible damage and halt disease progression.
Lymphatic-Venous Anastomosis (LVA)
This micro-surgical procedure connects lymphatic vessels to veins, reducing pressure and improving lymphatic flow. LVA is most effective when performed early, before significant tissue damage occurs. The procedure typically takes about an hour and requires minimal recovery time.
Lymph Node Transfer
In more advanced cases, lymph nodes are transplanted to areas affected by lymphedema. This helps restore lymphatic drainage and reduce swelling. While this method is suitable for later stages, it may not completely reverse tissue changes but offers significant symptom relief over time.
Combination with Conservative Therapies
Surgery can be complemented with compression therapy and physiotherapy to enhance results. These therapies improve circulation, reduce swelling, and maintain the benefits of surgical treatment.
Preventive Measures
Patients undergoing cancer treatments should consider preventive diagnostics within six months post-treatment. Identifying risks early allows for timely interventions, potentially avoiding lymphedema altogether.
Improving Quality of Life
Modern surgical techniques for lymphedema not only address physical symptoms but also restore confidence and mobility. Functional reconstruction, such as lymph node transfer combined with breast reconstruction, is transformative for patients post-cancer treatment.